Premium PSA Adsorbents
Deep technical understanding leads to best performance
UNICAT offers a premium range of Pressure Swing Adsorbents (PSA) and a deep technical understanding in engineering PSA systems to lead our customers to the best performance possible.

- Innovation
- Flexible Manufacturing
- Supply Chain Stability
We have the expertise to provide:
- Existing plant assessments
- Plant improvement recommendations
- Full Plant Design & Build
- Innovative Control Systems
- A complete range of Engineering Services
- A premium range of PSA Adsorbents
- Process Simulation


Ground-breaking gas purifying and separating technology
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) is a well-established gas separation process in hydrogen purification, helium purification and air separation among others. In addition to engineering, the adsorbents selected and employed in the PSA process are extremely important in determining the performance of a PSA unit.
We can provide a complete design and build package for your PSA System coupled with our premium range of adsorbents. Our range of products remove targeted contaminants from standard:
- CO, CO2, C1-C6+ hydrocarbons
- H2S, H2O
Different layers of adsorbents are used to remove targeted contaminants
There are a significant number of contaminants that require removal from a standard gas stream. Different layers of adsorbents are commonly used to remove one or more targeted contaminants.
Process steps are upflow while the regeneration steps are downflow.

PSA Benefits
- Downstream Catalyst poisoning avoided
- Benefits of Magcat® embedded with PSA result in increased SMR production, reduced Methane Slip
- Single source supplier (Catalyst, tubes, HTS, Purification, Sulfur removal & PSA)
- Significant PSA reload experience
- Responsive tech services & support
- Long Adsorbent Life
- High Purity Hydrogen Produced (99.99%)
- High hydrogen recovery (90%)
- Hydroprocessing units – Increased run time
Our services
- CO and N2 removal
- CO2, CO and H2S removal
- H2S, CS2 and CO2 removal
- H2O and heavy hydrocarbon removal
- Rapid liquid absorption
- Existing plant assessments
- Plant improvement recommendations
- Full Plant Design & Build capabilities
- Innovative Control Systems
- A complete range of Engineering Services


Optimized PSA Systems Solutions
We offer an innovative design and build package for your PSA System which can be coupled with our premium range of adsorbents. We formed a partnership with a leading plant design and manufacturer. This partnership is additive to our existing PSA adsorbent and control systems technology, facilitating reduction in customer process problems and increasing customer profitability.
Find out more through our UNICAT Technologies site.
Product Steps
I. Adsorption [ADSo]n
The adsorption phase is operated at high and constant pressure. This is determined by the pressure of the feed. The goal is the enrichment of the less selectively adsorbed species in the gas phase in the product. In this phase, the most rapidly adsorbed species such as H2O, Hydrocarbons, N2, CO2, and CO are selectively adsorbed. During the ad–sorption step, the feed valve as well as the H2 product valve remain open delivering high purity H2. Once this step is finished the depressurizations steps will follow.
II. Equalization [EQ]
The high and low-pressure beds are connected through their product ends. The main purpose of the Equalization step is to conserve mechanical energy that is contained in the gas of the high-pressure bed, as well as preserve part of the separation carried out in the high-pressure bed. With this step, blowdown reduce losses, with consequent improvement in the recovery of the product.
III. Provide Purge [PP]
The provide purge is a depressurization step in concurrent direction to purge or regenerate another absorber with a rich H2 stream during its regeneration phase.
IV. Bed Blowdown [BD]
The Bed Blowdown is the first step in which Tail gas valves are open and releases the impurities by the depressurization phenomena.
V. Receive Purge
Receive Purge is the final stage to clean the beds. A flow from another adsorbate in the Provide Purge step is used to final purge and regenerate the bed, directing all remaining contaminants to the tail gas system.
VI. Repressurization [REP]
Since the adsorption step is carried out at high pressure, the bed must first be repressurized. This is done by using streams coming from other adsorber beds in their equalization step.
VII. Final Repressurization [FR]
The last part of the repressurization is called Final Re–pressurization. This is either done by feed or H2 product.
Products

UNICARBON-HRU
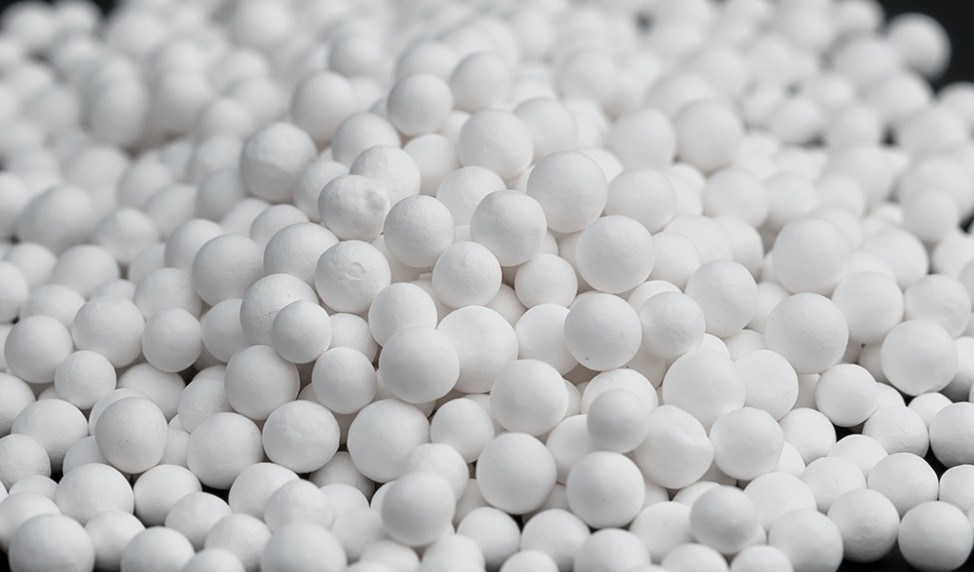
UNICAT's type HRU is a standard density activated carbon manufactured from butiminous carbon by high temperature steam activation under rigidly controlled conditions. The main characteristics of this activated carbon are high hardness and high macro-porosity makes it a versatile choice for many vapor-phase applications. The carbon is especially effective for removing weakly adsorbed compounds and for reducing emissions to trace levels. It has a high working capacity for CO2 when used in H2 pressure swing adsorption (H2 PSA) applications.

UNICARBON-HRU-CS
UNICAT’s UNICARBON-HRU-CS is a coconut shell based activated carbon for vapor phase applications. UNICARBON-HRU-CS is designed to remove light hydrocarbons (C1 – C4) and bulk CO2 in hydrogen purification PSA applications. Coconut shell based activated carbon is a versatile choice for many vapor-phase applications, because of its superior hardness and high micro-porosity. UNICARBON-HRU-CS is especially effective for removing weakly adsorbed compounds and for reducing emissions to trace levels.

UNIMOL HN
UNICAT’s UNIMOL-HN molecular sieve absorbents are made with the sodium form of zeolite with a pore opening of 10 angstroms. UNIMOL-HN is an excellent adsorbent for removing carbon dioxide, water, hydrogen sulfide and other weak polar molecules. UNIMOL-HN has a strong specialty binder which permits multiple regeneration cycles and pressure swings and therefore, a long run life in a PSA absorbent.

UNIMOL-5NPSA
UNICAT’s UNIMOL-5NPSA molecular sieve absorbents are made with the calcium-sodium form of zeolite with a pore opening of 5 angstroms. The strong ionic forces of the divalent calcium ion in UNIMOL-5NPSA are an excellent adsorbent for removing carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide and other weak polar molecules. UNIMOL-5NPSA has a strong specialty binder which permits multiple regeneration cycles and pressure swings and therefore, a long run life in a PSA absorbent.

SGAX-W
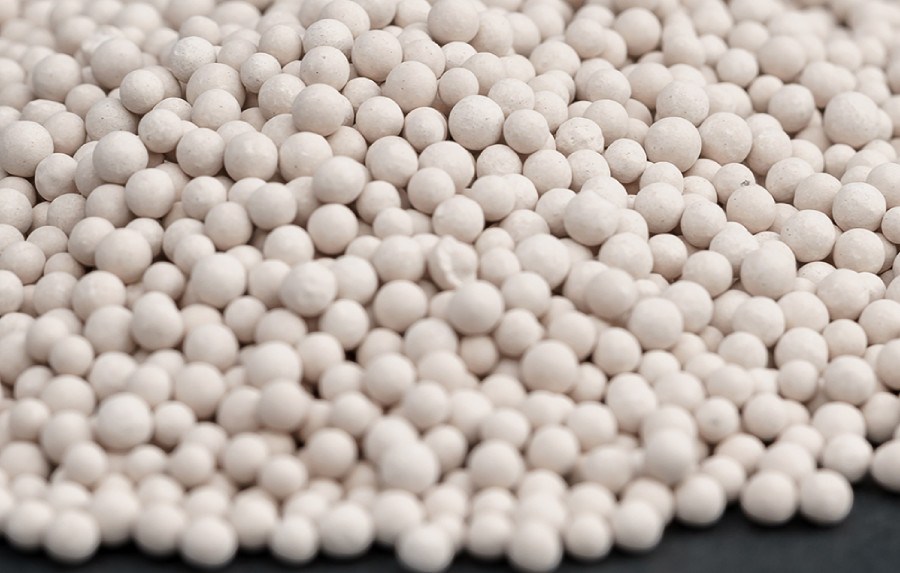
UNICAT’s SGAX-W series are type H beaded Silica gels with exceptionally large macro pores and binder technology to allow for capture of free water on top of absorbent beds without incurring physical damage and degradation. SGAX-W is to be used on top of all SGAX beds used in dehydration service.

SGAX
UNICAT’s SGAX beaded Silica Gels are type A high purity designed for removal of high levels of moisture for various feedstocks. The products exhibit high moisture retention, good structural integrity, and low pressure drops.

WR-11
UNICAT's WR-11 is a high performance, high porosity, high surface area activated alumina desiccant. WR-11 is used to remove water and water vapor from compressed air and a wide range of gas streams.
